- Teacher: Benedict Iorzer Labe
Labe's Sandbox Classroom
Available courses
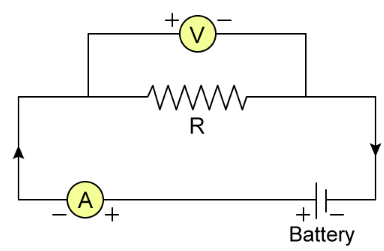
This course introduces students to the fundamental concepts of electrical quantities, including voltage, current, resistance, and power. It emphasizes understanding these quantities as the foundation of electricity, with clear explanations and practical examples. Students will also be guided through Ohm’s Law, expressed as V = IR, using simple circuit illustrations to show the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
In addition, the course explores practical applications where learners calculate unknown values in circuits and carry out experiments using resistors, lamps, and meters. It further explains the limitations of Ohm’s Law, particularly in non-ohmic devices such as diodes and filament lamps. To ensure safe learning, the course also highlights essential safety precautions to observe during electrical experiments, helping students gain both theoretical knowledge and hands-on skills while prioritizing safety.
Topic: Ohm’s Law and Its Applications
Sub-Topics
1. Review of Electrical Quantities
o Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Power.
2. Statement of Ohm’s Law
o V = IR, with illustrations using circuits.
3. Applications
o Calculating unknown quantities in simple circuits.
o Practical experiments with resistors, lamps, and meters.
4. Limitations of Ohm’s Law
o Non-ohmic devices (diodes, filament lamps).
5. Safety Precautions in Electrical Experiment.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this class, learners should be able to:
1. Define voltage, current, write their units of measurements and instruments used in taking measurements.
2. Define resistance, power, write their units of measurements and instruments used in taking their measurements.
3. Mention at least three factors affecting the resistance of a material
4. State Ohms law and it’s mathematical expression.
5. Calculate the unknown quantities in a simple circuit.
6. List at least three limitations of ohms law and safety precautions when working on electric circuit.
- Teacher: Dorathy Nonyelum Eze
- Teacher: Benedict Iorzer Labe